Cybersecurity Awareness Training for Employees

By OpenVPN Team
Employees are a company’s greatest asset — but they can also be a company’s greatest security risk.
Many employees have the best of intentions, but even the smallest mistakes can lead to big problems. That is why regular cybersecurity training for employees is so important.
There are several key areas where you should focus your company’s training efforts. Here are the types of cybersecurity training for employees that should be conducted annually, and some handouts that you can pass out to your employees as reminders throughout the year.
Email security training
Email is an important part of company operations but is also a major source of cybersecurity threats. Incoming emails can contain malware, and inappropriate email usage can expose vital business intelligence to your company’s competition. Employees need to know how to identify potentially dangerous emails and know which types of attachments are unsafe to open. Make sure to hold cybersecurity training for employees annually regarding how to protect their email accounts against cybersecurity threats, and consider hosting separate training sessions on how to use the email system properly to limit the release of important information. As a supplement, you can also distribute handouts that staff members can use as references throughout the year to stay compliant with email security policies.

Internet security training
The internet presents one of the biggest and most diverse threats to system security that your company will face. There are countless sources of malware, viruses, hackers, and other threats that can take advantage of your company’s inconsistent internet security policies to steal your information. Employees need to be using secure passwords, remaining cautious with what they share on the internet, and updating their machine software regularly. Employees also need periodic cybersecurity training to be updated as new threats are always developing. Each year, your company should hold a training session to demonstrate how employees should and shouldn’t use the internet at work. This includes explaining various types of threats, as well as setting guidelines for internet use on company computers and networks.
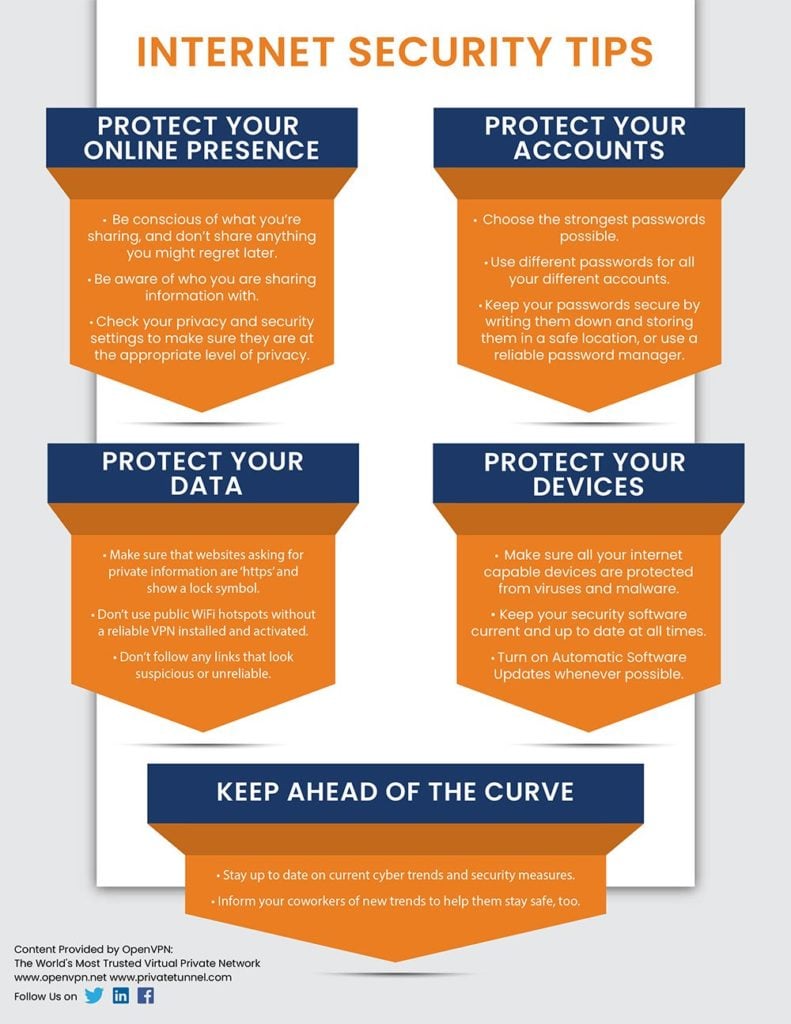
Information sharing procedures
While malware, viruses, and hackers are a big risk for your information security, your employees are actually a much more likely source of risk. Think about it: your employees have access to your company’s vital information. If they don’t know how to protect that information while performing their duties, it’s likely that they will expose that information to the wrong people. Employees need to be reminded about the company-approved methods for sharing information securely. Teach your staff members how to send information through secure methods, and let them know what information can be sent to external sources. Host periodic cybersecurity training for employees to help them understand how to protect the information while remaining effective at their jobs. Focus on teaching them how to recognize what information can and cannot be used, as well as which channels to use for each.

Remote work best practices
 Organizations all around the world are increasingly embracing remote work. And why shouldn’t they? Remote work is an easy way to decrease expenses and access top talent regardless of geographic location. It is also a free benefit for employees that allows greater work-life balance — leading to increased productivity, retention, and morale. It’s a win/win for many organizations, so it’s not surprising that remote work is quickly becoming the new norm. But like with every new work model, there needs to be policies and guidelines in place. Make sure your remote teams know what is expected of them. Make sure your employees are using a VPN whether they are at home or in an airplane. Do your employees know which information can or cannot be displayed on their screen while hanging out at the coffee shop? Do they know how to properly handle and secure their devices when away from their home office? Thinking through all of these different components and making sure your workers are aware will greatly reduce the risks. And remember: there is no “one size fits all” policy when it comes to remote work. Your business is unique, so the policies you build and the training you provide to remote workers needs to be unique as well.
Organizations all around the world are increasingly embracing remote work. And why shouldn’t they? Remote work is an easy way to decrease expenses and access top talent regardless of geographic location. It is also a free benefit for employees that allows greater work-life balance — leading to increased productivity, retention, and morale. It’s a win/win for many organizations, so it’s not surprising that remote work is quickly becoming the new norm. But like with every new work model, there needs to be policies and guidelines in place. Make sure your remote teams know what is expected of them. Make sure your employees are using a VPN whether they are at home or in an airplane. Do your employees know which information can or cannot be displayed on their screen while hanging out at the coffee shop? Do they know how to properly handle and secure their devices when away from their home office? Thinking through all of these different components and making sure your workers are aware will greatly reduce the risks. And remember: there is no “one size fits all” policy when it comes to remote work. Your business is unique, so the policies you build and the training you provide to remote workers needs to be unique as well.

Password security
An OpenVPN Survey discovered that 25% of employees use the same passwords for absolutely everything. They might get used to using a particular password for their email account, and then implement that for all of their work passwords as well. This means if a bad actor gets access to an employee’s email password, there is a good chance they can use that password to access other corporate services that are protected by that same password. On top of that, a lot of employees also use short, easy to guess passwords that a brute-force attack could crack in a matter of seconds. To prevent this from happening, make sure your employees are aware of what constitutes a strong password.
Passwords should always be three things:
- Long
- Complex
- Not Easy To Guess
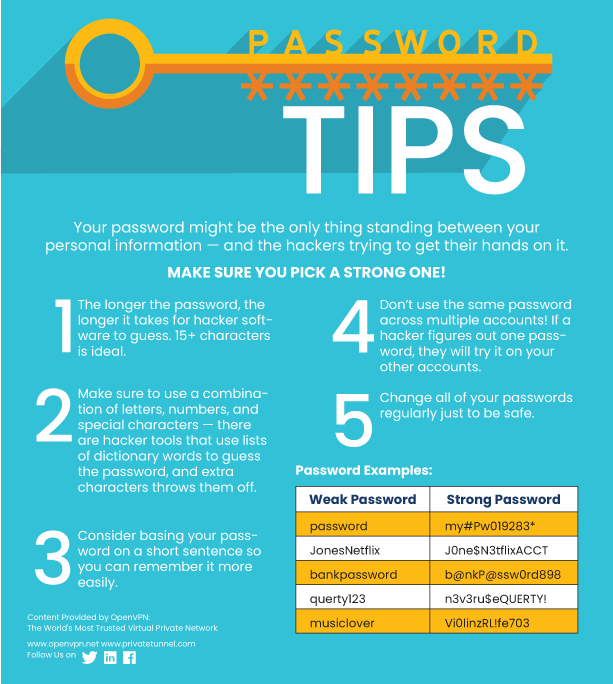
The password should consist of a minimum of eight characters (but 12+ is preferred!) that includes a healthy mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Passwords also need to be different from account to account. If your employees know these guidelines and apply them, your chances of a breach will be reduced.
Cybersecurity training for employees is an essential part of maintaining your company’s security systems; your team needs to understand how to use the appropriate procedures to ensure that your systems stay secure. To improve your company’s cybersecurity, plan training annually and provide your employees with helpful resources and reminders throughout the year. And remember that even with regular training, there is a good chance your staff will fall out of the appropriate practices throughout the year. Make sure you have additional lines of defense in place for if and when employees revert back to risky habits.
How companies use OpenVPN to prevent internal threats
DevSquad is a company that specializes in providing tailor-made and innovative on-demand software. They handle a wide range of projects — from computer vision to industrial printers, and from product prototyping to regression testing. Although headquartered in Utah, the company’s remote workforce connects from all over. The company needed a solution to provide its team with secure ways to connect to corporate servers and client servers, as well as essential resources within the private cloud. As a security-conscious firm, they set up a bastion host to provide access, but without a reliable VPN, DevSquad relied on a community username/password system — that was not as secure or effective as they wanted.
DevSquad recognized that despite training and policies, some employees just won’t choose strong enough passwords, and they needed a better way to ensure the people accessing the network were who they said they were. The company started looking for a solution to securely connect their remote workforce while providing easy ways to implement access control and end-point authorization measures such as two-factor authentication.
OpenVPN Access Server provided DevSquad with an easy way to keep the company’s remote workforce connected. The company downloaded Access Server on AWS using Terraform, which made it easy for DevSquad to implement. OpenVPN Access Server was launched on an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) within its Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Remote employees can connect to the VPN and gain access to network resources within the VPC — and Devsquad can protect their cloud networking services within their VPC without granting public access.
To meet their access control and end-point authorization needs, DevSquad enabled two-factor authentication (2FA) for all of their clients and employees. By implementing 2FA, attackers are less likely to successfully impersonate employees or clients to gain access to devices and networks containing sensitive business resources. OpenVPN Access Server allows DevSquad to take care of business securely and effectively, with a much lower risk of network intrusion.

.png)

